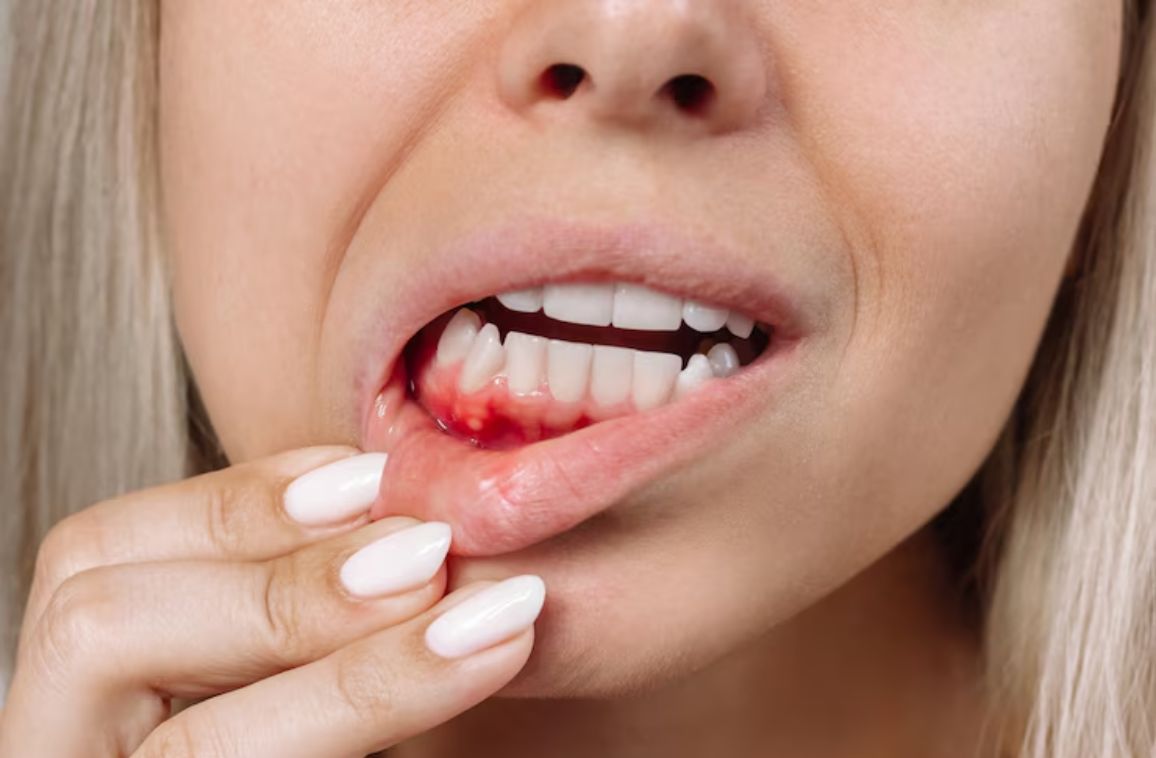
Bleeding gums are awesome, as they are caused by brushing the teeth too vigorously or even wearing dentures that do not fit properly. This health problem can be a common symptom of gum disease or other health issues.
Frequent gum bleeding is a serious condition that needs medical attention. The problem includes:
- Periodontitis (an advanced form of gum disease).
- Leukemia (cancer of the blood).
- Lack of clotting cells (platelets).
- Vitamin deficiency.
Dental conditions that can lead to bleeding gum causes:
Dental care issues are indeed the primary cause of bleeding gums. Gingivitis (inflammation of the gums) and periodontitis do make the gums sensitive and also prone to bleeding.
Gingivitis
Most people develop gingivitis when plaque stays on gum lines for too long. Plaque does refer to the debris and bacteria that stick to one’s teeth.
Brushing one’s teeth does remove plaque and can prevent a person from developing cavities (dental caries). But plaque can stay on one’s gum line if the person does not brush and floss properly.
If plaque is not removed, it can harden into tartar (calculus), which will indeed increase bleeding. The accumulation of plaque near one’s gums can also cause gingivitis.
Periodontitis
Periodontal disease (periodontitis) can occur when gingivitis has advanced. Periodontal disease is, of course, an infection of the gums, jawbone, and other supportive tissues that do connect one’s teeth and gums. Periodontitis can cause the teeth to loosen or fall out.
Vitamin deficiencies
Vitamin C and vitamin K deficiencies can cause gums to bleed easily. The doctor needs to check levels of vitamins C and K if you have bleeding gums that are not due to improper dental care. A diet containing both nutrients ensures healthy teeth.
Other bleeding gum causes
People who use dentures can experience bleeding gums. This is more likely to happen if the dentures fit too tightly.
Talking to the dentist or orthodontist if dentures or other oral appliances are causing the gums to bleed does help.
Pregnancy also often causes gum bleeding. Hormonal changes that tend to occur during pregnancy can cause the gums to be more sensitive.
Bleeding disorders such as hemophilia and leukemia can also increase the risk of bleeding gums. The gums might bleed more often if taking blood-thinning medications. Drugs in this category include warfarin, aspirin, and heparin.
Treatment of bleeding gums
Good dental hygiene is the initial step to managing bleeding gums.
Visit the dentist twice per year for professional cleaning, as it helps maintain healthy gums. The dentist can inform well if faced with gingivitis and teach how to brush the teeth properly. Proper brushing and flossing can indeed remove plaque from one’s gum line and also reduce the risk of developing periodontal disease.
The dentist can also show how to use an antiseptic mouthwash to minimize plaque that can form in one’s mouth. And a rinse of warm salt water does help soothe swollen gums that do bleed easily.
Using a soft toothbrush is a good idea. It will be gentle on inflamed gums, especially if experiencing bleeding after brushing one’s teeth. Medium and hard bristles can be very abrasive for one’s delicate gums.
People with gum problems can also use an electric toothbrush. The specially designed brush heads of the toothbrushes help to clean the gum line more easily than a manual toothbrush.
Conclusion
Schedule an appointment with a primary care provider to determine whether dental health is the underlying cause of bleeding gum. This seems a way out of ensuring proper dental hygiene. A physical examination and blood work can no doubt help determine the cause of one’s bleeding. Treatment will indeed vary according to one’s condition.


